Understanding Linux File Permissions: A Guide to chmod, chown, and chgrp
Understanding Linux File Permissions: A Guide to chmod, chown, and chgrp
Managing file permissions is one of the most important skills for Linux and DevOps engineers.
Incorrect permissions = broken deployments, security issues, and Permission denied errors.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- What Linux permissions mean
- How to read permission notation
- How to use
chmod,chown, andchgrpwith real examples
What Are Linux File Permissions?
Every file in Linux has three types of access:
| Access Type | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Read (r) | View file content / list folder |
| Write (w) | Modify file / add-remove inside folder |
| Execute (x) | Run executable/script or enter directory |
And permissions apply to three owner levels:
| Level | Who it affects |
|---|---|
| Owner (u) | User who owns the file |
| Group (g) | Members of assigned group |
| Others (o) | Everyone else |
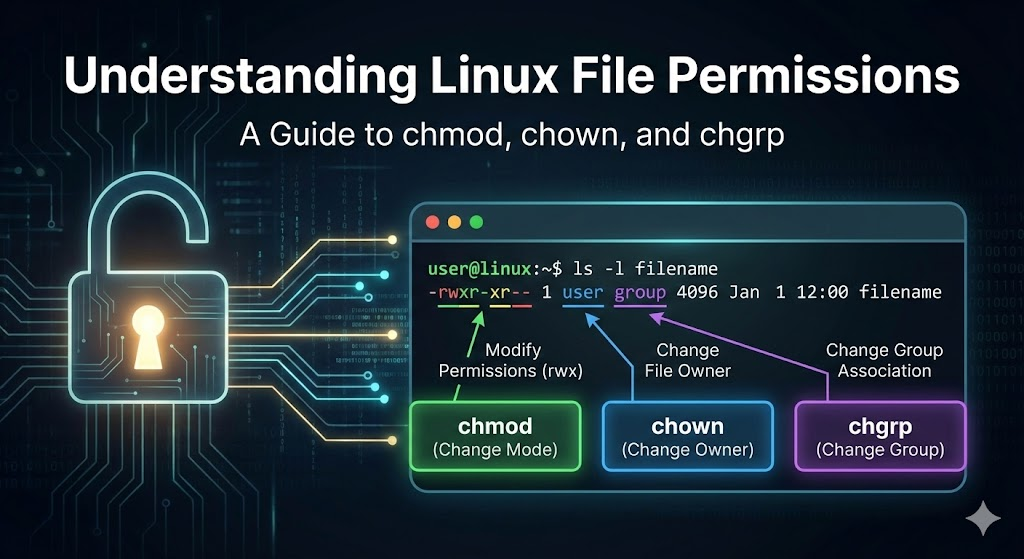
How to View Permissions
ls -lExample output:
-rwxr-x--x 1 ubuntu devops 1024 Jan 10 script.shBreakdown:
| Section | Meaning |
|---|---|
- | File type (- = file, d = directory) |
rwx | Owner permissions |
r-x | Group permissions |
--x | Others permissions |
ubuntu | Owner user |
devops | Owner group |
script.sh | File name |
chmod — Change File Permissions
Symbolic mode (u/g/o + add/remove = ±)
chmod u+x script.sh # give execute to owner
chmod g-w app.log # remove write from group
chmod o-r secrets.env # prevent others from reading
chmod ug+r config.yaml # allow owner & group to readNumeric Mode (octal notation)
r = 4 w = 2 x = 1
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 7 | rwx |
| 6 | rw- |
| 5 | r-x |
| 4 | r– |
Example:
chmod 755 script.sh # Owner rwx, group r-x, others r-x
chmod 600 id_rsa # Only owner can read/write (secure SSH key)Recursive apply
chmod -R 755 /var/www/app # apply to all files/subfolderschown — Change File Owner & Group
Change owner only:
chown ubuntu script.sh # set user as ownerChange owner & group:
chown ubuntu:devops script.shRecursive owner change:
chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/appCommonly used for web servers (nginx / apache)
chgrp — Change Group Ownership
chgrp devops file.txt # assign group to file
chgrp -R devops /data # apply recursivelyUseful when multiple users share same project directory.
Quick Security Tips
✔ Restrict sensitive files ✔ Avoid chmod 777 🚫 (full access to everyone — dangerous!) ✔ Use groups for shared access ✔ Always check permissions before production deploys
